Introduction
Genetic variation or polymorphism
The regular and simultaneous occurrence in a single interbreeding population of two or more discontinuous genotypes. The concept includes differences in genotypes ranging in size from a single nucleotide site (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) to large nucleotide sequences visible at a chromosomal level.
Basic classes of DNA variation
- Insertion-Deletion Length Polymorphism (INDEL)
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
- Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) Length Polymorphism (Mini- and Micro- Sattellites)
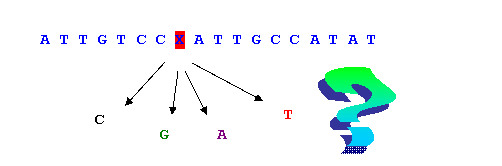
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Importance of genetic variation analysis
- early diagnosis, prevention and treatment of human diseases
- systematics and taxonomy
- population, quantitative, and evolutionary genetics
- plant and animal breeding
- identifying individuals and populations (paternity and forensic analysis)
SNP genotyping technologies
Primer Extension
- Common Primer Extension (CPE) reaction, a method for SNP genotyping that involves
annealing a primer to 3' end of DNA fragment adjacent to a SNP site followed by its extension using dideoxynucleotide terminators (ddNTPs)
to preven further incorporation of nucleotides. The identity of the extended base is determined either by fluorescence or mass
to reveal SNP genotype.
- Arrayed Primer Extension (APEX) is a variant of SPE where primers are attached to a solid support through their 5' ends and reaction is performed under solid phase conditions.
- Allele-Specific Primer Extension (ASPE) uses extension of allele-specific primers with PCR amplified template, and the extended products are analyzed for fluorescence to determine SNP genotype.
Hybridization
- Gene Chip® array (Affymetrix, CA)
- TaqMan® genotyping assay (Applied Biosytems) combines hybridization and 5' nuclease activity of polymerase coupled with fluorescence detection.
Ligation
Enzymatic cleavage
Other methods
- BeadArrayTM (Illumina) combines hybridization, primer extension, and ligation for generating allele-specific product followed by PCR amplification.
Probe
Resources





