|
TaqMan®
|
TaqMan® Gene Expression
Introduction
Applied Biosystems developed
TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays, a genome-wide collection of quantitative, standardized assays for gene expression analysis by
real-time quantitative RT-PCR. The TaqMan® Assay utilizes the 5' nuclease activity of Taq
DNA polymerase to cleave a fluorescently labeled probe (FAMTM-labeled MGB).
These assays are a family of more than 700,000 primer/probes sets, which have been pre-designed by using a state-of-the-art, extensively validated (~20,000 assays were functionally tested) bioinformatics pipeline. Assays for quantification of gene-encoded transcripts are available for Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Rattus norvegicus, Drosophila melanogaster, Arabidopsis thaliana, Canis familiaris, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Macaca mulatta.
TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays Design Pipeline
TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays Design Pipeline
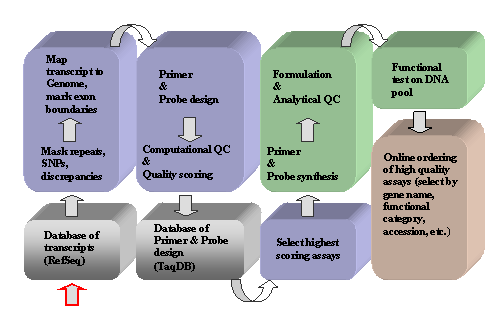
Automated Primer/Probe Design Pipeline. This figure highlights the design pipeline and rigorous quality checks that the TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays must pass.
Methods
- Source of transcripts
- Transcript pre-processing
- Repetitive and low complexity regions in each transcript are masked (i.e., nucleotides are replaced by "N").
- The masked transcripts are mapped to the NCBI genome assemblies with an Applied Biosystems proprietary alignment tool. The positions of each exon-exon boundary are marked for each multi-exon transcript; single-exon transcripts are identified as such.
- All known SNPs sites are masked after performing a BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Tool) analysis against the NCBI and Celera SNP database.
- Assay design
- Each assay includes a single FAMTM dye-lebeled TaqMan® probe with a minor groove binder (MGB) moiety and two unlabeled oligonucleotide primers.
- These components are designed with a program called TaqExpress, which takes into account optimal melting temperature (Tm)
requirements, GC-content, buffer/salt conditions, oligonucleotide concentrations, secondary structure, optimal amplicon size, reduction of primer-dimer formation, etc.
- In case of multi-exon transcripts, probes are placed at each exon-exon boundary to ensure that the primers bind in two distinct exons and that the fluorescent signal is only generated from correctly spliced templates.
- In silico quality scoring
- Transcript BLAST scoring
Determining the degree of homology, through BLAST, between the assay and other related transcripts. A penalty is assigned if an assay detects any closely homologous transcripts other than the intended target.
- Genome BLAST scoring
A penalty is assigned if an assay hits other physical locations on the genome in addition to the location of the target gene.
- Intron size scoring
A penalty is assigned when the assay is designed across an exon-exon boundary that spans a small intron (i.e., <2 kb).
- Only high quality assays are selected for manufacture and made available on the website.
- Relational database for 5' nuclease assay designs (TaqDB)
- Information
about transcripts, assays, global relationships between
transcripts and assays, exon-intron structure, in silico QC,
manufacturing order status, and analytical QC data determined
in the manufacturing process are maintained in a relational database at Applied Biosystems. Data from expression studies in
select RNA tissue pools are also stored in this database.
- Remapping
- Because transcript databases change over time (new transcripts are added, current transcripts may be revised or removed),
Applied Biosystems regularly remaps the assays to NCBI transcript database.
Probe
Resources
Disclaimer
Mention of specific products or vendors on this website does not constitute
an endorsement by the U.S. government.
|





