|
 |
||||||
   |
|
|
dCAPS
|
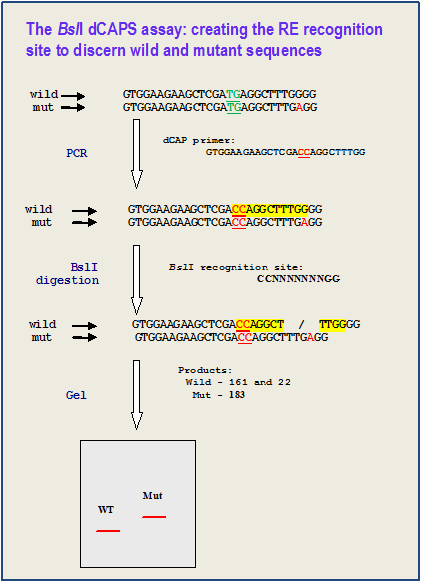
Derived Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences (dCAPS)IntroductionThe Derived Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequences (dCAPS) assay is a modification of CAPS (or alternatively, PCR-RFLP) technique for detection of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs). In dCAPS assay a mismatches in PCR primer are used to create restriction endonuclease (RE)-sensitive polymorphism based on the target mutation. This technique is useful for genotyping known mutations and genetic mapping of isolated DNAs. Similar to the CAPS technique, this method is simple, relatively inexpensive, and uses the ubiquitous technologies of PCR, restriction digestion and standard agarose gel electrophoresis. How It Works The dCAPS technique introduces or destroys a restriction enzyme recognition sites by using primers that containing one or more micmatches to the template DNA. The PCR product modified in this manner is then subjected to restriction enzyme digestion and the presence or absence of the SNP is determined by the resulting restriction pattern. Example
Applications of dCAPS primers
ProbeSample Queries
ReferencesNeff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE. dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J. 1998 May;14(3):387-92. PMID: 9628033 ResourcesPubMed query: Note: [MAJR] is a Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) tag for Major Heading. The tag is used to limit the search to articles for which major subjects are represented by terms included in the NLM MeSH database. DisclaimerMention of specific products or vendors on this website does not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government. |
Questions or Comments?
E-mail the NCBI Service Desk