|
 |
||||||
   |
|
|
RFLP
|
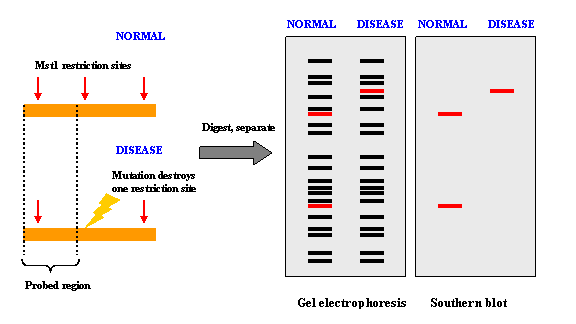
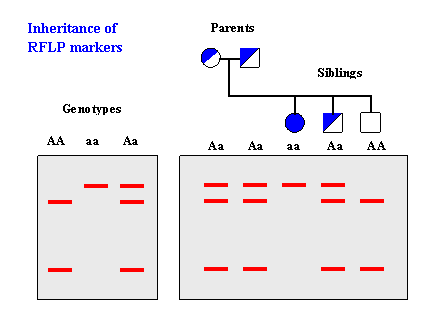
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)IntroductionRestriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) is a difference in homologous DNA sequences that can be detected by the presence of fragments of different lengths after digestion of the DNA samples in question with specific restriction endonucleases. RFLP, as a molecular marker, is specific to a single clone/restriction enzyme combination. Most RFLP markers are co-dominant (both alleles in heterozygous sample will be detected) and highly locus-specific. An RFLP probe is a labeled DNA sequence that hybridizes with one or more fragments of the digested DNA sample after they were separated by gel electrophoresis, thus revealing a unique blotting pattern characteristic to a specific genotype at a specific locus. Short, single- or low-copy genomic DNA or cDNA clones are typically used as RFLP probes. The RFLP probes are frequently used in genome mapping and in variation analysis (genotyping, forensics, paternity tests, hereditary disease diagnostics, etc.). How It Works
SNPs or INDELs can create or abolish restriction endonuclease (RE) recognition sites, thus affecting quantities and length of DNA fragments resulting from RE digestion. Genotyping
Developing RFLP probes
PCR-RFLP Isolation of sufficient DNA for RFLP analysis is time consuming and labor intensive. However, PCR can be used to amplify very small amounts of DNA, usually in 2-3 hours, to the levels required for RFLP analysis. Therefore, more samples can be analyzed in a shorter time. An alternative name for the technique is Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequence (CAPS) assay. ProbeSample QueriesResourcesPubMed query: Note: [MAJR] is a Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) tag for Major Heading. The tag is used to limit the search to articles for which major subjects are represented by terms included in the NLM MeSH database. DisclaimerMention of specific products or vendors on this website does not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government. |
Questions or Comments?
E-mail the NCBI Service Desk