|
 |
||||||
   |
|
|
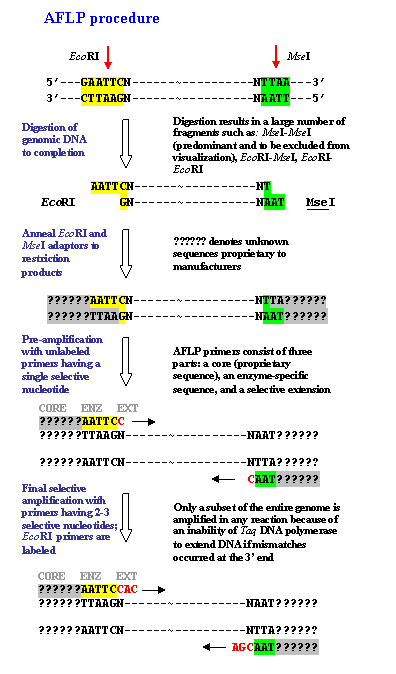
AFLP
|
Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP)IntroductionAmplified Fragment Length Polymorphisms (AFLPs) are differences in restriction fragment lengths caused by SNPs or INDELs that create or abolish restriction endonuclease recognition sites. The AFLP technique is based on the selective PCR amplification of restriction fragments from a total digest of genomic DNA. How It Works
Using 3-bp selective primer extensions gives 128 possible linker combinations. Therefore, 128 subsets of genomic DNA can be readily amplified. Thus, thousands of markers can be generated quite rapidly. Weaknesses of AFLP
ProbeSample QueriesReferences» Vos P, et al. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Nov 11;23(21):4407-14. PMID: 7501463 ResourcesPubMed query: Note: [MAJR] is a Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) tag for Major Heading. The tag is used to limit the search to articles for which major subjects are represented by terms included in the NLM MeSH database. DisclaimerMention of specific products or vendors on this website does not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government. |
Questions or Comments?
E-mail the NCBI Service Desk